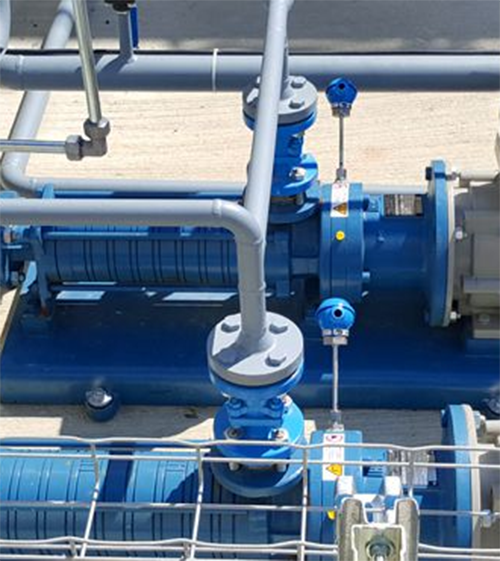
Solution: Liquefied gas container
Solution: Liquefied gas container
General information
In Austria, tanks with a volume of 1 m³ to 1000 m³ are in use. These are differentiated according to the type of installation and the corrosion protection measures:
-
- Above-ground tanks with paint coating
- Underground or partially underground tanks with epoxy resin coating (according to DIN 4681) and cathodic corrosion protection (mandatory from 1.6.2020 for all LPG tanks in operation).
- Underground or partially underground tanks with bitumen coating (according to DIN 30673) and cathodic corrosion protection.
- LPG tanks are subject to the Pressure Equipment Act DGG BGBl. No. 161/2015 and must be inspected at regular intervals by an accredited inspection body in accordance with ISO 17020. After passing the inspection, the containers receive a test plan chain and may continue to be operated.
- Containers without a plan chain will no longer be filled by the liquefied petroleum gas supplier (DGÜW-V §49 Para. 8).
Regulations and downloads
- Pressure Equipment Act, DGG BGBl. No. 161/2015
- Pressure Equipment Monitoring Ordinance, DGÜW-V BGBl. No. 165/2015
- Pressure Vessel Installation Ordinance, DBA-VO BGBl. II No. 361/1988
- Dual Pressure Equipment Ordinance, DDGV Federal Law Gazette II No. 59/2016 Link to RIS
- Liquid Gas Ordinance, FGV Federal Law Gazette II No. 446/2002
- Ordinance on the Monitoring of Liquefied Petroleum Gas Conversion Vessels
- Federal Law Gazette II No. 172/2013
- Liquid Gas Filling Station Ordinance, FGTV BGBl. II No.247/2010
- ÖVGW Guideline G2 – Technical Rules for Liquefied Petroleum Gas
- ÖVGW Guideline G7 – Liquefied petroleum gas piping systems; Piping systems for liquefied petroleum gas with operating pressures above 500 mbar up to and including 25 bar
- ÖVGW Guideline G B331 – Operation and maintenance of cathodic corrosion protection systems for underground natural gas pipelines made of steel
- Information folder “Liquid gas systems
Accreditation
The following tests are carried out on LPG containers:
- First operational test after the container has been placed on the market, consisting of an external inspection supplemented by a check of the legal placing on the market and an initial assessment of the installation.
- External inspection, consisting of an assessment of the installation, a visual inspection to assess damage, leaks and corrosion. In the case of buried tanks, the assessment of the walls is carried out with the aid of the cathodic corrosion protection test.
- Internal examination and pressure test is carried out in the form of an acoustic emission test.
- Check of the cathodic corrosion protection, consisting of the determination of the protective current and potential measurements with the aid of a reference electrode.
Inspection intervals for liquid gas containers
The inspection intervals for LPG containers are regulated in the special provisions of the Pressure Equipment Monitoring Ordinance BGBl. II No. 420/2004 as amended by BGBl. II No. 165/2015, Annex 3:
Liquid gas tanks up to 13 m³
- Every 3 years External inspection
- every 12 or 15 years Internal examination and pressure test (acoustic emission test)
The deadlines for the main inspection depend on the “quality” of the vessel and are determined by the inspection body on the basis of the vessel documents (pressure vessel inspection book, declaration of conformity).
Liquid gas tanks over 13 m³
- Every 3 years External examination
- every 12 years internal examination and pressure test (acoustic emission test)
Cathodic corrosion protection
- Every 3 years Inspection of KKS plant
- Annual intermediate inspection of external power KKS plants (according to ÖNORM EN 13636 and ÖVGW guideline G B 331, both declared binding in the DGÜW-V)